
On July 13, Clarivate Analytics released the latest ESI statistics, which showed that the discipline of Molecular Biology & Genetics entered the top 1% of ESI Global Ranking for the first time. This marks that NJUCM has entered the international high-level ranks in this discipline, which is another eye-catching achievement of the university's overall discipline construction. At present, NJUCM has boasted six disciplines including Pharmacology and Toxicology, Clinical Medicine, Chemistry, Biology and Biochemistry, Neuroscience and Behavior, Molecular Biology and Genetics among the top 1% of ESI, of which Pharmacology and Toxicology into the ESI top 1‰. So far, the number of ESI top 1% and ESI top 1‰ disciplines of NJUCM has taken the lead of all the Chinese medicine colleges and universities in China.
Among the 22 disciplines in ESI statistics, NJUCM has published 11,227 high-level international papers, including 95 ESI highly cited papers. In the disciplines of Molecular Biology and Genetics, NJUCM has published 781 papers with 15,576 citations and an average citation frequency of 19.94 times.
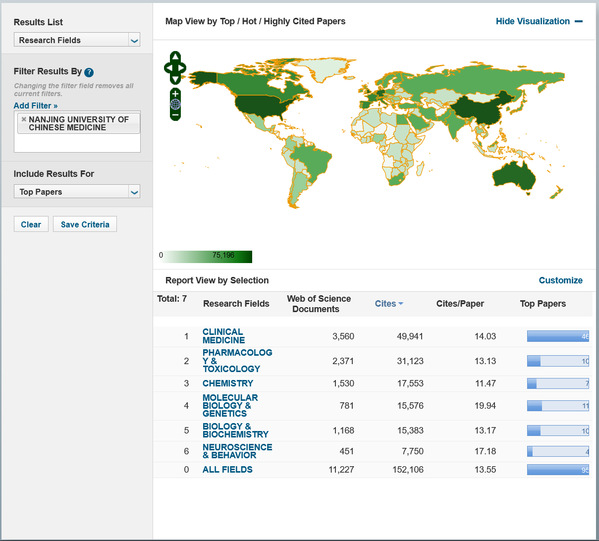
Data related to the 6 ESI top 1% disciplines of NJUCM.
NJUCM has been actively practicing the mission of interpreting the principles of Chinese medicine with modern science, continuing to promote the construction of the first-class Chinese medicine discipline group with Chinese Pharmacology as the core, and vigorously strengthening the basic, cross and emerging disciplines. A number of important collaborative research results have been published in top journals of Molecular Biology and Genetics, such as Nature, Science, Cell Research, Autophagy, etc., which have contributed to the realization of high-level scientific and technological self-reliance and self-improvement, the creation of a new track for innovative development of TCM disciplines, and the shaping of new driving force and advantages in the development of Chinese medicine.




